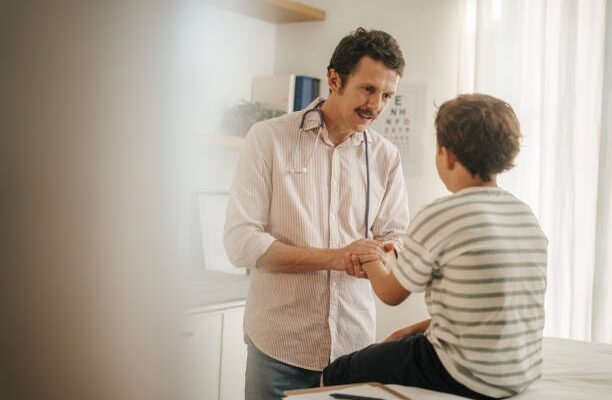
Children can experience anxiety just like adults, but they often lack the language or tools to express it. For parents, noticing the early signs and understanding treatment options is essential. Anxiety treatment for kids requires a thoughtful, age-appropriate approach that considers emotional, social, and behavioral development.
Recognizing Anxiety in Children
Anxiety in kids doesn’t always look the same as it does in adults. Common signs include:
- Trouble sleeping
- Avoiding social situations
- Excessive worry or fear
- Frequent physical complaints (stomachaches, headaches)
- Difficulty concentrating
In many cases, these symptoms can overlap with other concerns like ADHD or depression, making it crucial to consider comprehensive evaluations.
Importance of ADHD Evaluation for Kids
Some children with anxiety may also show signs of attention difficulties. An ADHD evaluation for kids helps determine if inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsiveness are affecting their daily lives. Misdiagnosed or overlooked ADHD can intensify anxiety, leading to greater frustration for both the child and parents.
A proper evaluation usually includes questionnaires, observation, behavioral assessments, and sometimes academic feedback. Understanding whether a child is facing anxiety, ADHD, or both can help guide the right treatment plan.

How Depression Treatment for Kids Ties In
Anxiety and depression often go hand in hand. While anxiety may cause excessive fear or worry, depression in children can appear as:
- Persistent sadness
- Low energy or motivation
- Withdrawal from activities they once enjoyed
- Changes in appetite or sleep
Depression treatment for kids typically includes therapy, emotional support, and sometimes medical intervention when necessary. Addressing depression alongside anxiety ensures a more holistic treatment approach.
Types of Anxiety Treatment for Kids
There are several effective options for treating childhood anxiety:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is one of the most proven methods for treating anxiety. It helps children identify their anxious thoughts and learn new ways to think and behave.
2. Play Therapy
For younger children, play therapy allows them to express feelings through toys and storytelling, helping therapists understand what they’re going through.
3. Parent-Child Interaction Therapy (PCIT)
This therapy strengthens the parent-child relationship and teaches parents skills to support emotional regulation and manage anxiety.
4. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Simple breathing exercises, meditation, and guided imagery can empower kids to manage their anxiety in the moment.
5. School-Based Support
Counselors and teachers can be part of the support system, helping to reduce school-related stressors and provide consistent encouragement.
Conclusion
Recognizing anxiety in children and seeking timely help is a powerful first step. Anxiety treatment for kids works best when it’s tailored to each child’s needs. Incorporating ADHD evaluations and keeping an eye out for signs of depression ensures a full-circle approach. With the right support and understanding, children can learn to manage their anxiety and thrive emotionally and academically.