Outpatient surgery has revolutionized healthcare by offering patients a faster and more cost-effective alternative to inpatient procedures. But for many, the pricing structure surrounding these surgeries remains confusing. From facility fees to Medicare coverage, knowing what you’re paying for is crucial. In this guide, we break down the major components that impact Outpatient Surgery Costs and provide tips to help you navigate the billing process.
What Is Outpatient Surgery?
Outpatient surgery, also known as ambulatory or same-day surgery, allows patients to go home on the same day of their procedure. These surgeries do not require an overnight hospital stay and are typically performed in outpatient surgery centers or specialized hospital departments.
Common outpatient procedures include:
- Cataract removal
- Hernia repairs
- Colonoscopies
- Arthroscopic joint surgeries
While convenient, outpatient procedures can still carry significant costs, depending on where and how they’re performed.

Key Factors That Influence Outpatient Surgery Costs
Understanding what contributes to the total cost of outpatient surgery is the first step toward making informed healthcare decisions. Below are the most common factors:
1. Type and Complexity of Surgery
Not all outpatient procedures are created equal. More complex surgeries often involve specialized staff, additional equipment, and extended recovery time, all of which increase the cost. For instance, a minor dermatological procedure will cost significantly less than a laparoscopic gallbladder removal.
2. Surgeon and Anesthesia Fees
Surgeon fees depend on their expertise, reputation, and geographical location. In addition, anesthesia is almost always required, and this brings in a separate fee for the anesthesiologist, which can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars depending on the procedure length and complexity.
3. Facility Fees for Outpatient Surgery
One of the most often misunderstood components is the facility fees for outpatient surgery. These charges cover the use of the operating room, equipment, nursing staff, supplies, and administrative overhead. Hospitals typically charge more than freestanding surgical centers due to their higher operating costs.
In many cases, patients find the facility fee to be the largest portion of their bill—sometimes even exceeding the surgeon’s fee.
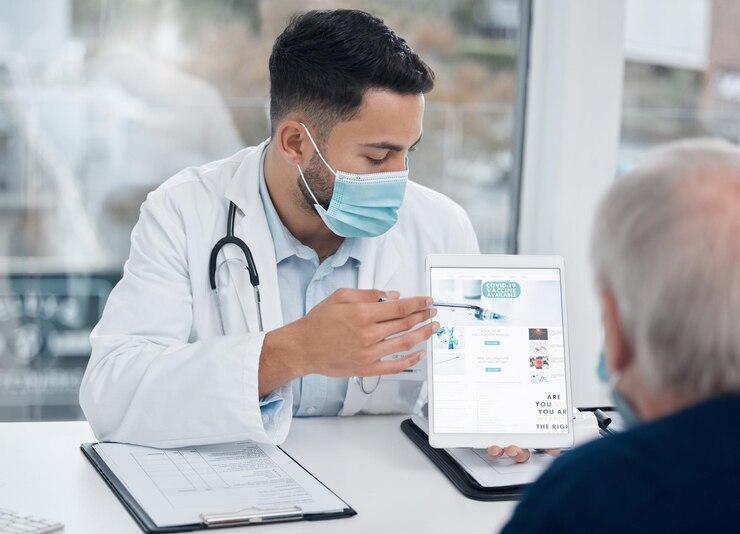
The Role of Insurance and Medicare
Insurance significantly affects what you will actually pay out-of-pocket. Here’s how:
1. Private Insurance
Most private insurers cover outpatient surgeries, but deductibles, co-pays, and network restrictions can impact final costs. Patients are advised to verify:
- If the facility is in-network
- Whether pre-authorization is needed
- The percentage of the cost covered by insurance
2. Medicare Coverage
Medicare generally covers medically necessary outpatient procedures under Part B. However, patients may still face 20% of the Medicare-approved amount, plus the facility fee, which is partially covered under Medicare’s Ambulatory Surgical Center (ASC) payment system.
Understanding what Medicare pays versus what you’re responsible for helps avoid unexpected bills after surgery.
Tips to Reduce Your Out-of-Pocket Costs
Managing healthcare costs requires some homework. Here are practical ways to keep your expenses in check:
1. Ask for a Cost Estimate
Before undergoing surgery, request a detailed cost estimate that includes surgeon, anesthesia, and facility fees. Most providers and surgical centers offer pre-surgery billing consultations.
2. Choose a Freestanding Surgery Center
Whenever medically appropriate, consider choosing an ambulatory surgery center instead of a hospital. These centers typically have lower overhead costs and can offer the same level of safety and care for routine procedures.
3. Review Your Insurance Coverage
Check your plan’s Summary of Benefits to understand deductibles, co-insurance, and out-of-pocket maximums. Confirm that all providers involved in your care are within your insurance network to avoid balance billing.
4. Look Into Payment Plans or Financial Assistance
If cost is a concern, ask if the provider offers interest-free payment plans or has a financial assistance program. Many facilities are willing to work with patients to arrange manageable payment terms.
Summary and Final Thoughts
Outpatient surgeries are a cost-effective and efficient solution for many medical conditions, but the pricing structure can be overwhelming. By taking the time to understand the breakdown of charges—including Outpatient Surgery Costs and facility fees for outpatient surgery—patients can make better decisions and avoid surprise bills.