how to lower your hemoglobin a1c

how to lower your hemoglobin a1c
Keeping your haemoglobin A1c levels under control is essential for preserving your general health, especially if you have diabetes. A measurement of your average blood sugar over the previous two to three months is called haemoglobin A1c, or HbA1c. Poor blood sugar regulation is indicated by a higher HbA1c level, which raises the risk of complications from diabetes. These are some practical methods for bringing your haemoglobin A1c down to a healthy level Here are effective strategies on how to lower your hemoglobin a1c.
Understanding Hemoglobin A1c
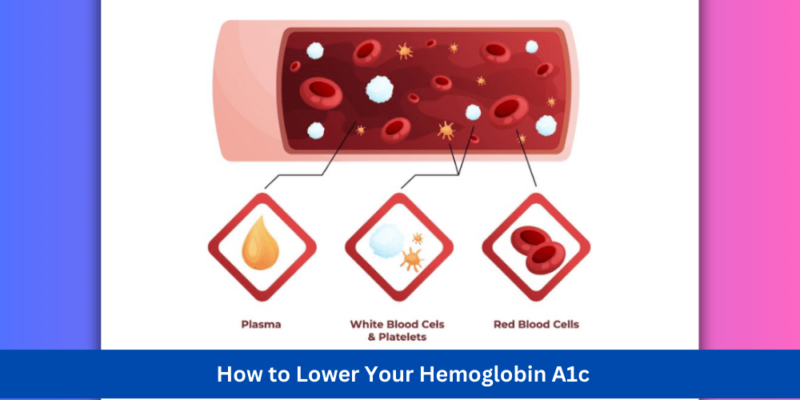
Understanding haemoglobin a1c is crucial before moving on to the strategies. When blood glucose binds to haemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells, haemoglobin A1c is created. Your A1c level will rise in proportion to your blood sugar levels because more glucose will bind to haemoglobin. Most diabetics want to maintain a HbA1c of less than 7%. Individual goals, however, could change depending on your health and your doctor’s recommendations.
Lifestyle Changes to Lower Hemoglobin A1c
- Adopt a Healthy Diet:Having a balanced diet is essential for controlling blood sugar. Make a point of eating a range of vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and good fats. Steer clear of sugary drinks and processed foods. Rather, choose foods with a low glycaemic index (GI), as these will affect blood sugar levels more gradually.
- Regular Exercise: Your body uses insulin more effectively when you exercise, which can lower your blood sugar levels. On most days of the week, try to get in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: You can better understand how various foods, activities, and medications affect your glucose levels by checking your blood sugar on a regular basis. Making educated decisions about your lifestyle and treatment plan requires knowledge of this information.
- Stay Hydrated: Maintaining blood sugar levels is facilitated by consuming lots of water. Elevations in blood sugar levels may result from dehydration. Try to have eight glasses of water or more each day.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels can be impacted by sleep deprivation. To help control your blood sugar levels, try to get between seven and nine hours of good sleep every night.
Medical Interventions
- Medication Adherence: Maintaining your HbA1c levels requires taking your diabetic medications as directed.Speak with your healthcare provider if you encounter any side effects or have questions about your medications.
- Insulin Therapy: Insulin therapy may be required for certain individuals with diabetes. Insulin taken as prescribed by your physician can dramatically lower HbA1c and blood sugar levels.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM):CGM devices provide real-time data by continuously monitoring your blood glucose levels during the day and night.This can assist you in promptly modifying your medication, exercise routine, and diet.
Stress Management
Blood sugar levels can be adversely affected by ongoing stress. Engage in stress-relieving activities like yoga, meditation, deep breathing, and outdoor time. It’s crucial to understand healthy stress management techniques in order to how to lower hemoglobin a1c.
Regular Check-ups
It’s crucial to see your healthcare provider on a regular basis. During these consultations, you can keep an eye on your HbA1c levels and modify your treatment plan as needed. Your healthcare provider can provide tailored guidance on how to lower hemoglobin a1c.
Must Read : Top Natural Remedies to Bring Blood Pressure Down 2024
Conclusion
Changing your lifestyle, receiving medical attention, and having frequent testing are all part of learning how to lower your hemoglobin a1c . You can successfully lower and maintain your HbA1c levels by implementing a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, drinking plenty of water, managing stress, sleeping enough, taking your medication, and visiting your doctor on a regular basis. Making these adjustments improves general health and well-being in addition to helping manage diabetes.